|
Remco systems can be utilized to
minimize the need for other types of treatment and
maintenance associated with these parameters. With the
proper pretreatment, water discharge can be reduced to a
small fraction of the present volume that will lower
treatment costs.
Usual treatments include:
 Water softening for hardness. Calcium
and Magnesium (hardness ions) are removed by the softening
process. Ca and Mg are exchanged for sodium ions on an ion
exchange resin. Hardness in water causes scale. Scale is
usually Calcium and/or Magnesium carbonate that precipitates
out as the ions are concentrated in the boiler. Chemicals
can be added to control scale but they can be reduced to a
very small quantity if a softener is used. Water softening for hardness. Calcium
and Magnesium (hardness ions) are removed by the softening
process. Ca and Mg are exchanged for sodium ions on an ion
exchange resin. Hardness in water causes scale. Scale is
usually Calcium and/or Magnesium carbonate that precipitates
out as the ions are concentrated in the boiler. Chemicals
can be added to control scale but they can be reduced to a
very small quantity if a softener is used.
 Pervaporation, a membrane process or
deaerator can be used to remove Oxygen and CO2 down to very
low levels for high pressure boilers. Only small amounts of
chemical oxygen scavengers are required after oxygen
removal. Pervaporation, a membrane process or
deaerator can be used to remove Oxygen and CO2 down to very
low levels for high pressure boilers. Only small amounts of
chemical oxygen scavengers are required after oxygen
removal.
 Silicates cause another type of scaling
and can be removed with ion exchange or a membrane process.
Membrane systems are preferred where dissolved ion
concentrations are high because of operating cost
considerations. High silicate levels are difficult and may
require co-precipitation with other ions or high temperature
caustic regeneration of ion exchange system. Silicates cause another type of scaling
and can be removed with ion exchange or a membrane process.
Membrane systems are preferred where dissolved ion
concentrations are high because of operating cost
considerations. High silicate levels are difficult and may
require co-precipitation with other ions or high temperature
caustic regeneration of ion exchange system.
 Dissolved solids can be removed by ion
exchange or Reverse Osmosis membrane processes. The results
are similar with ion exchange able to remove practically all
the ions and RO able to get very close with lower operating
and maintenance costs. With high TDS concentrating, a
combination of the two can be very cost effective. The
advantage of removing dissolved solids is that you can
greatly increase the time between blow downs as the makeup
water is almost void of solids. It takes much longer to get
to the concentration when the boiler should be blown. Dissolved solids can be removed by ion
exchange or Reverse Osmosis membrane processes. The results
are similar with ion exchange able to remove practically all
the ions and RO able to get very close with lower operating
and maintenance costs. With high TDS concentrating, a
combination of the two can be very cost effective. The
advantage of removing dissolved solids is that you can
greatly increase the time between blow downs as the makeup
water is almost void of solids. It takes much longer to get
to the concentration when the boiler should be blown.
 Suspended solids are removed by
filtration. Normally, you would want a backwashing filter
followed by a fine cartridge filter for the best results.
The backwashing filter can take high solids loading before
flows are reduced and is self cleaning. The polishing filter
makes sure any residual material does not get through. Suspended solids are removed by
filtration. Normally, you would want a backwashing filter
followed by a fine cartridge filter for the best results.
The backwashing filter can take high solids loading before
flows are reduced and is self cleaning. The polishing filter
makes sure any residual material does not get through.
 Concentration of organics are less of a
problem in a properly designed feedwater system because much
less chemistry is required to maintain the boiler. It is
much easier to balance the system, and in some systems, no
oxygen scavenger is required. Concentration of organics are less of a
problem in a properly designed feedwater system because much
less chemistry is required to maintain the boiler. It is
much easier to balance the system, and in some systems, no
oxygen scavenger is required.
Remember, a good water analysis is you best friend. We will
ask you for a water analysis. Print out the attached form if
you don't know what you need to measure.
Boiler Water Quality Links:
Boiler Water Treatment: Lessons Learned (US Army)
Minimize Boiler Blow down
Improving Steam System Performance: A Sourcebook for
Industry
Steam Handbook: Chapter 2, Water Treatment
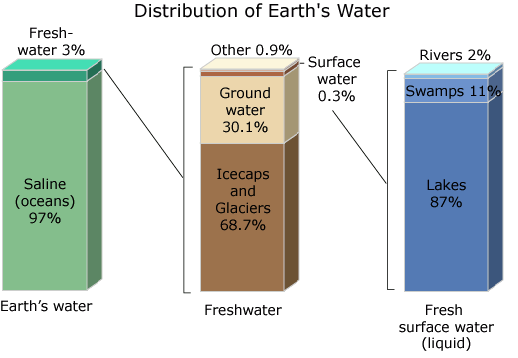
As it is seen from the above diagram only 3.0% of earths
water is fresh water. Out of this only 30.1 % & 0.3 % is
useable.
No water, irrespective of the original source, should be
assumed to be completely free of contamination & pollution.
These contaminations may be natural or man made. The common
contaminations, impurities & pollution in water are odor,
tastes, colour, turbidity, suspended solids, organic and
inorganic pollutants like pesticides, insecticides,
herbicides, VOCs, dissolved gases, dissolved solids, heavy
metals, domestic, chemical & industrial waste, bacteria,
virus, Water Treatment is a Physical & Chemical process for
making water suitable for human consumption and other
processes.
As contaminations and pollutions of water are different,
treatment required depend upon nature of contamination. Most
of the times combinations of treatment technologies are used
to treat water.
Water purification is the process where microbiological
contamination is controlled. Again various technologies are
used for water purification.
Application areas where water & water treatment is
required :
 Human consumption :
Human consumption :
Drinking, cooking, bathing, washing, cleaning etc.
 Process Industries :
Process Industries :
Package drinking water plants, Food, hotel, medicine,
pharmaceutical, laundry, cooling towers, boilers, swimming
pool, molding machines, different manufacturing units, aqua
cultures, construction, etc.
 Different Technologies used as Water Treatment &
Purifications :
Different Technologies used as Water Treatment &
Purifications :
Sedimentation, Coagulation, filtration, activated carbon,
chemical disinfection, conditioning, softening, ion
exchange, ultra violet, reverse osmosis, ozonation,
List of Contaminants & their MCL :
 Microorganisms
Microorganisms
 Disinfectants
Disinfectants
 Disinfection Byproducts
Disinfection Byproducts
 Inorganic Chemicals
Inorganic Chemicals
 Organic Chemicals
Organic Chemicals
 Radionuclides
Radionuclides
|
Micro organisms
| Contaminant |
MCLG1
(mg/L)2 |
MCL or TT1
(mg/L)2 |
Potential Health Effects
from Ingestion of Water |
Sources of Contaminant in
Drinking Water |
| Cryptosporidium (pdf file) |
zero |
TT 3 |
Gastrointestinal illness
(e.g., diarrhea, vomiting, cramps)
|
Human and fecal animal
waste |
| Giardia lamblia |
zero |
TT 3 |
Gastrointestinal illness
(e.g., diarrhea, vomiting, cramps) |
Human and animal fecal
waste |
| Heterotrophic plate count |
n/a |
TT 3 |
HPC has no health effects;
it is an analytic method used to measure the
variety of bacteria that are common in
water. The lower the concentration of
bacteria in drinking water, the better
maintained the water system is. |
HPC measures a range of
bacteria that are naturally present in the
environment |
| Legionella |
zero |
TT 3 |
Legionnaire's Disease, a
type of pneumonia |
Found naturally in water;
multiplies in heating systems |
| Total Coliforms (including
fecal coliform and E. Coli) |
zero |
5.0%4
|
Not a health threat in
itself; it is used to indicate whether other
potentially harmful bacteria may be present5 |
Coliforms are naturally
present in the environment; as well as
feces; fecal coliforms and E. coli only come
from human and animal fecal waste. |
| Turbidity |
n/a |
TT3 |
Turbidity is a measure of
the cloudiness of water. It is used to
indicate water quality and filtration
effectiveness (e.g., whether disease-causing
organisms are present). Higher turbidity
levels are often associated with higher
levels of disease-causing microorganisms
such as viruses, parasites and some
bacteria. These organisms can cause symptoms
such as nausea, cramps, diarrhea, and
associated headaches. |
Soil runoff |
| Viruses (enteric) |
zero |
TT3 |
Gastrointestinal illness
(e.g., diarrhea, vomiting, cramps) |
Human and animal fecal
waste |
|
| |
|
Disinfectants
| Contaminant |
MRDLG1
(mg/L)2 |
MRDL1
(mg/L)2 |
Potential Health Effects from
Ingestion of Water |
Sources of Contaminant in
Drinking Water |
Chloramines (as Cl2)
|
MRDLG=41 |
MRDL=4.01 |
Eye/nose irritation; stomach discomfort,
anemia |
Water additive used to control microbes
|
| Chlorine (as Cl2) |
MRDLG=41 |
MRDL=4.01 |
Eye/nose irritation; stomach discomfort |
Water additive used to control microbes |
| Chlorine dioxide (as ClO2) |
MRDLG=0.81 |
MRDL=0.81 |
Anemia; infants & young children:
nervous system effects |
Water additive used to control microbes |
|
| |
|


